Introduction
Occasionally, you may wish to modify a property that doesn’t conform to standards. Maybe you’re looking to build beyond the required setbacks, add an additional unit, or put something in that isn’t normally allowed. In all these cases, you would require consent from the city, likely in the form of a minor variance.
What is a Minor Variance?
A minor variance is approval is given for a small deviation from the prevailing Zoning by-laws. Legally, consent is required to navigate away from (or vary) from the governing by-laws in a city or town. In some cases, the municipality can grant these approvals without having to change or re-zone the property. Minor variances are governed by The Planning Act, section 45.
The 4 Tests
According to The Act, the municipality must use four tests, or questions, to determine if the application is minor.
The four tests of a Minor Variance are:
- Does the city consider the application minor?
- Does the application benefit the development of lands or improve them?
- Generally, is the application inside the “intent” of the Zoning By-Law?
- Would the approval conform with the city’s existing Official Plan?
Granted, the four tests used are quite vague and ambiguous. Each municipality can use a degree of subjectivity when determining if a variance is minor.
COMMITTEE OF ADJUSTMENT
The Committee of Adjustment reviews and approves applications. The committee will schedule a hearing and give notice to neighbours. According to the Planning Act, all neighbours within 60 metres must receive notice at least 10 days in advance.
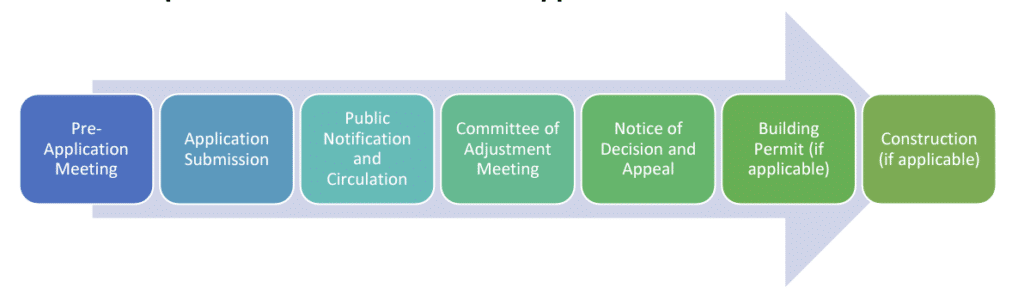
Following the hearing, the committee must issue a notice of decision within 10 days. Within the following 20 days, the applicant or neighbours can appeal the decision before the municipality deems it final. The Ontario Land Tribunal hears and decides on appeals.
Wrapping it Up: The Minor Variance in Everyday Life
Minor variances can affect property value both negatively and positively. For the receiver, a deviance from the required by-law can improve property value. Conversely, some by-laws help maintain property value, and a variance could negatively impact a neighboring property’s worth. If you have a specific question with respect to minor variances, be sure to Contact Us.